Lev Vygotsky is a Russian psychologist who is best known for his development of the Social Constructivism theory. According to About’s website, constructivism is a type of learning theory that explains human learning as an active attempt to construct meaning in the world around us. Vygotsky’s social constructivism theory suggest that knowledge is constructed during our interactions with others that includes peers, teachers and other adults in our environment. Based on his theory, inside the classroom interactions with others, shapes the individual students skills and abilities valued by his or her culture. Which lead to Vygotsky’s argument that language is the main tool that promotes thinking, developing reasoning, and supporting cultural activities such as reading and writing. For example, Vygotsky noticed that children were able to solve problems with their speech, as well as with their eyes and hands through interactions with others. He suggested that language helps children be strategic, rather than purely impulsive, in their approach to complex problems, and it helps them gain control over their thinking and behavior (Vygotsky, 1978).
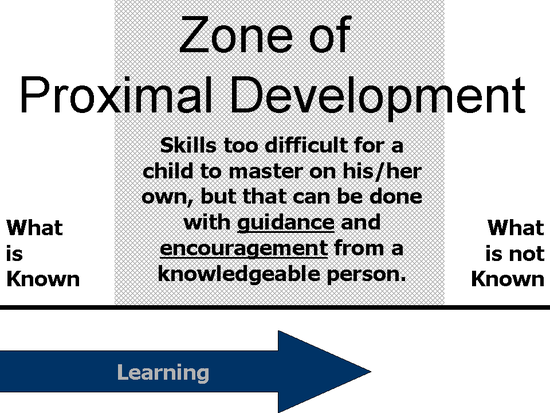
After language has played a major part in a student’s early stages of life that includes infancy to preschool, it is imperative to expose them to the learning process around the age of five. Thus, implementing Vygotsky's theory would allow a Kindergarten teacher to model and demonstrate expected behavior in the classroom. Once instruction has been given, a teacher can then assess the student's prior knowledge of content information based on his or her environment prior to being exposed to the learning process. This information gather allows the teacher to develop and provide instruction based on his or her curriculum. Nonetheless, this drives the teacher's lesson and unit plans based on the assessment gathered from one's classroom demographics. The lesson and unit plans will disseminate content information through direct instruction, small group instruction, and peer interaction. As the teacher facilitates throughout the classroom, a student can be provided with one-on-one instruction or peer buddy assistance to a student that his struggling with content information in a particular lesson or activity. This is where Vygotsky's created the zone of proximal development (ZPD). ZPD indicates to the educator that the learner needs assistance in applying and connecting information one has learned. For example, an English teacher would model or demonstrate to the student how to ask questions and engage in discussions or provide the student with an opportunity to engage in peer discussion through a group activity. This is the area between what the student is able to do independently and where he or she may need assistance. Vygotsky’s theories of learning and development is put into four major framework which includes: 1) children construct knowledge 2) learning can lead to development 3) development cannot be separated from social context and 4) language plays a central role in mental development. These remaining four frameworks drives Vygotsky's theory on how knowledge lies in our interactions with one another and our environment.
Source for the below image: http://explorable.com/images/zone-of-proximal-development.gif
After language has played a major part in a student’s early stages of life that includes infancy to preschool, it is imperative to expose them to the learning process around the age of five. Thus, implementing Vygotsky's theory would allow a Kindergarten teacher to model and demonstrate expected behavior in the classroom. Once instruction has been given, a teacher can then assess the student's prior knowledge of content information based on his or her environment prior to being exposed to the learning process. This information gather allows the teacher to develop and provide instruction based on his or her curriculum. Nonetheless, this drives the teacher's lesson and unit plans based on the assessment gathered from one's classroom demographics. The lesson and unit plans will disseminate content information through direct instruction, small group instruction, and peer interaction. As the teacher facilitates throughout the classroom, a student can be provided with one-on-one instruction or peer buddy assistance to a student that his struggling with content information in a particular lesson or activity. This is where Vygotsky's created the zone of proximal development (ZPD). ZPD indicates to the educator that the learner needs assistance in applying and connecting information one has learned. For example, an English teacher would model or demonstrate to the student how to ask questions and engage in discussions or provide the student with an opportunity to engage in peer discussion through a group activity. This is the area between what the student is able to do independently and where he or she may need assistance. Vygotsky’s theories of learning and development is put into four major framework which includes: 1) children construct knowledge 2) learning can lead to development 3) development cannot be separated from social context and 4) language plays a central role in mental development. These remaining four frameworks drives Vygotsky's theory on how knowledge lies in our interactions with one another and our environment.
Source for the below image: http://explorable.com/images/zone-of-proximal-development.gif